Landsat, arguably, the most successful Earth Observation satellite series in the world, launched its 9th satellite on 27 September, 2021.
It was launched with an Atlas rocket from the Space Launch Complex 3E, Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, USA, into an altitude of about 700 kilometres.
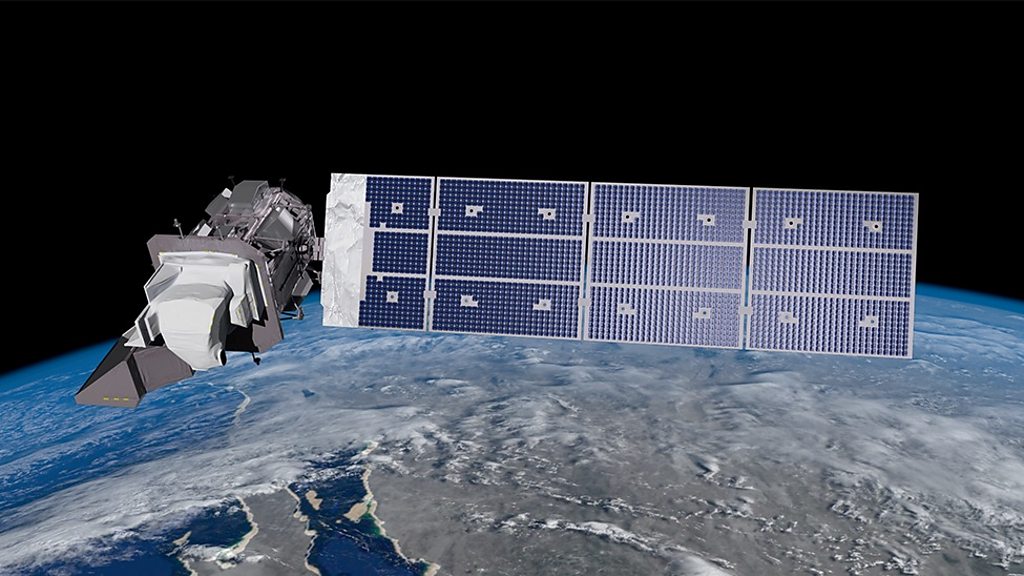

The satellite with a launch mass of 2,711 kg (5,977 lb) was the 2,000th rocket launch in that launch site.
The Landsat constellation has been useful in the last 40 years in remote sensing operations, notably on the shrinking of Lake Chad which is now 10% of its original size.
Non-stop images from American Landsat 1 from 1972 to 1978, Landsat 2 from 1975 to 1982, Landsat 3 from 1978 to 1983, Landsat 4 from 1982 to 1993, Landsat 5 from 1984 to 2013, Landsat 7 from 1999 and Landsat 8 from 2013, showed the true picture of the lake over time – re-establishing the Landsat programme as the longest Earth observation mission in the world (Landsat 6 was launched on October 5, 1993 on a Titan II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, but failed to reach orbit).
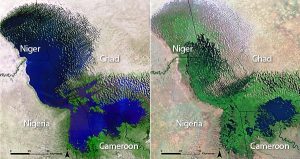
A lake which provides economic livelihood to 30 million people has shrunk by at least 90%.
Its images are free of charge.
Landsat, a series of earth-observing satellites, is jointly managed by NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
photo credit: bbc